Are you sometimes confused between the terms East Asia and Far East? And Western Asia and Middle East? Does Asia Pacific include India?
The boundaries of these regions depend on the context in which they are framed, e.g., geographic, political or economic. In addition, some international corporations refer to the world markets with other terms.
No standard definition precisely outlines the Middle East, it is generally accepted as comprising the countries of the Arabian Peninsula, Cyprus (Europe), Egypt (Africa), Iraq, Iran, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestinian territories, Syria, and Turkey. «West Asia is growing in popularity as a neutral, non-Eurocentric synonym for the Middle East» state National Geographic.
«Near East is a dated term that may be used in historical references» according to Wikipedia. «Use the terms Far East and Orient with caution. Asia or East Asia are more neutral terms» suggests National Geographic.
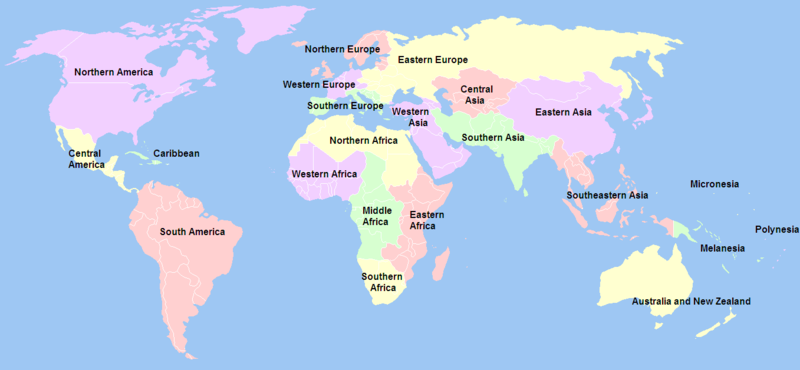
After some online research, the UN geoscheme (the Statistics Division of the United Nations) seems to be the fairest and clearest. United Nations defines subregions as a part of a larger region or continent and it is usually based on location.
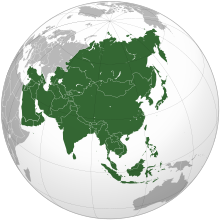
By the UN geoscheme the Asia continent is divided in the following subregions:
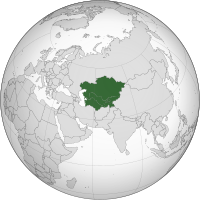
– Central Asia
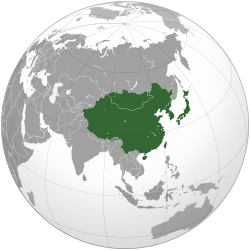
– Eastern Asia
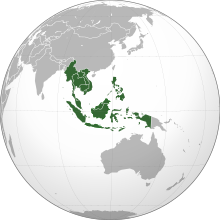
– South-East Asia
– Southern Asia

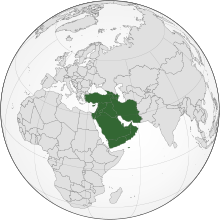
– Western Asia
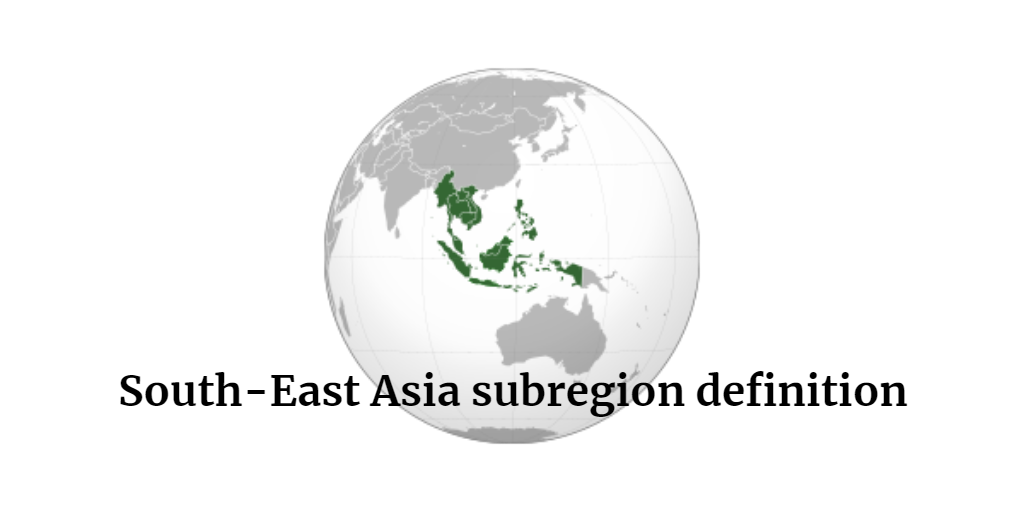
South-East Asia subregion definition:
«Southeast Asia generally consists of Asian countries south of China and east of India, including Brunei, Cambodia, East Timor, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam» according to the Statistics Division of the United Nations.

